In a world where unforeseen circumstances can disrupt lives and livelihoods, long-term disability insurance emerges as a crucial financial safety net. This coverage, often overlooked in the whirlwind of everyday life, acts as a vital shield against the economic fallout of debilitating injuries or illnesses. It’s a testament to the reality that life can take unexpected turns, and having a plan in place can make all the difference when facing a prolonged inability to work.
This guide delves into the intricate world of long-term disability insurance, unraveling its purpose, key features, and the crucial role it plays in safeguarding your financial well-being. We’ll explore the factors to consider when choosing a policy, the application process, and the steps involved in claiming benefits. Understanding the nuances of this type of insurance can empower you to make informed decisions and protect yourself against the uncertainties of the future.
Understanding Disability Insurance
Disability insurance provides financial protection in the event you become unable to work due to an illness or injury. It can help replace lost income, allowing you to focus on your recovery without the added stress of financial hardship.
Types of Disability Insurance
Disability insurance policies can be categorized based on their duration and coverage.
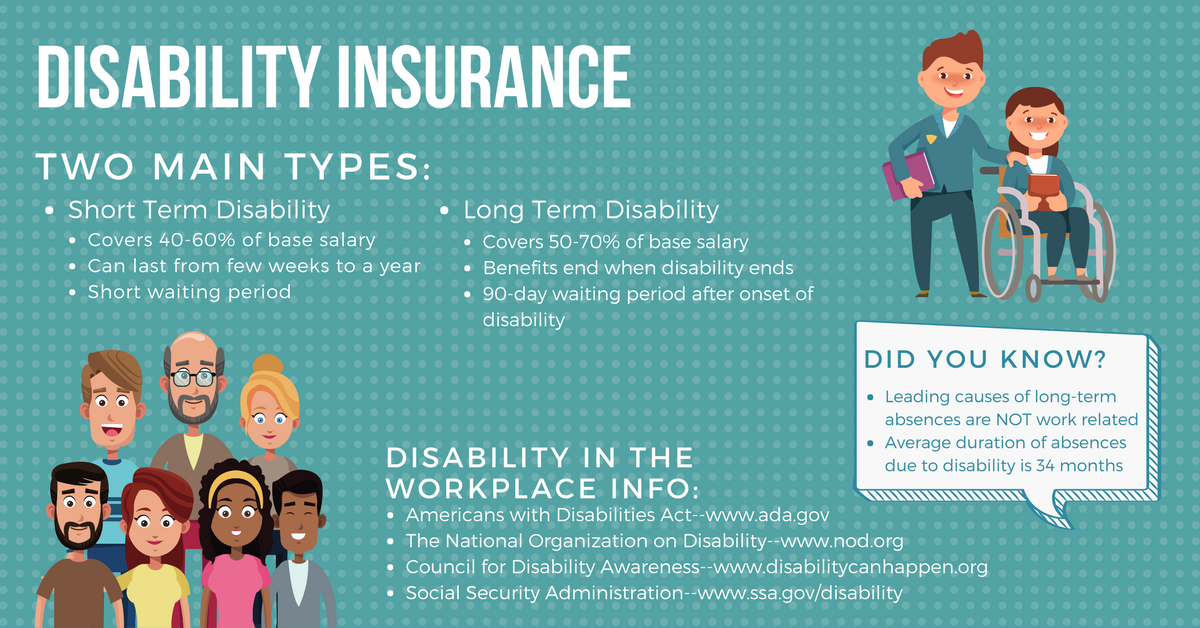
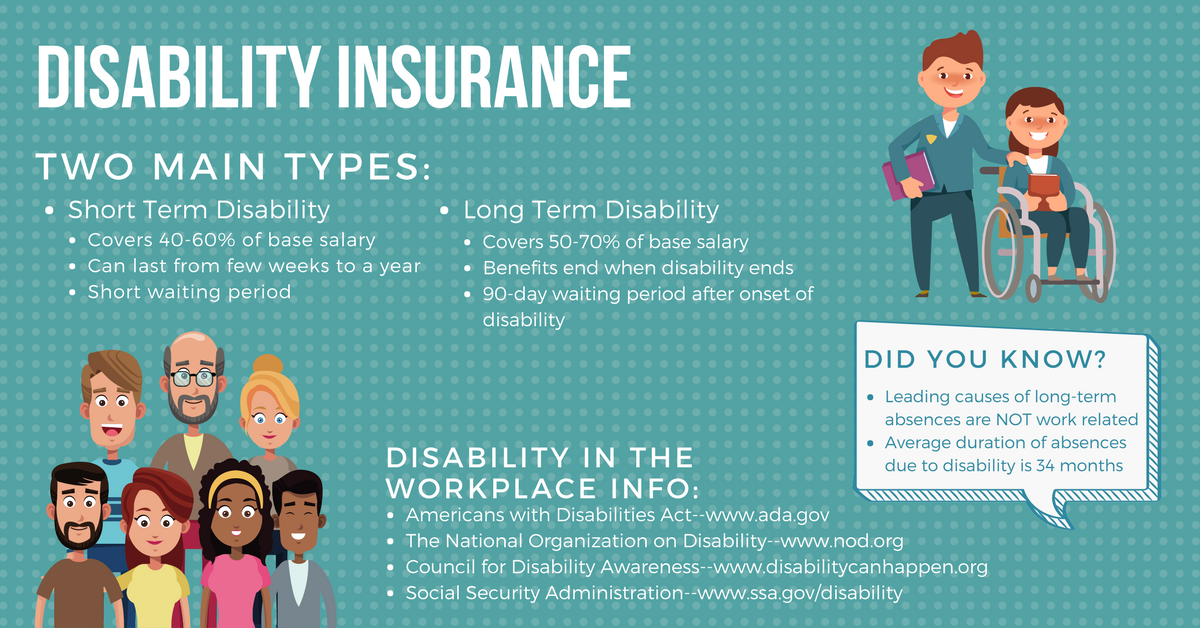
- Short-Term Disability Insurance: This type of insurance typically provides benefits for a limited period, usually 3 to 6 months. It is often offered by employers as part of a benefits package and is designed to cover temporary disabilities.
- Long-Term Disability Insurance: This type of insurance provides benefits for a longer duration, often until retirement age or for a specific period, such as 5 or 10 years. It is typically purchased by individuals and can be used to cover long-term disabilities that prevent you from working for an extended period.
Real-Life Scenarios
Disability insurance can be a valuable asset in various situations.
- A construction worker sustains a back injury: A construction worker involved in an accident may be unable to perform their job for an extended period. Long-term disability insurance can provide financial support during their recovery and rehabilitation, allowing them to focus on healing without worrying about their income.
- A teacher is diagnosed with a chronic illness: A teacher diagnosed with a chronic illness might experience periods of disability requiring time off work. Disability insurance can help ensure their income is covered during these periods, allowing them to focus on their health and well-being.
Long-Term Disability Insurance
Long-term disability (LTD) insurance is a type of insurance that provides financial protection if you are unable to work due to a disability. It typically pays a monthly benefit to replace a portion of your lost income, helping you maintain financial stability during a challenging time.
Coverage Period
LTD insurance policies generally cover a period of time that extends beyond the coverage provided by short-term disability insurance. The duration of coverage varies depending on the policy, but it often extends for a significant period, such as two years, five years, or until the age of 65. Some policies may even provide lifetime coverage.
Eligibility Criteria and Waiting Periods
To be eligible for LTD benefits, you must meet certain criteria, such as:
- Having a qualifying disability, as defined by your policy.
- Having worked for a specific period of time before becoming disabled.
- Meeting the policy’s waiting period, which is the time you must be disabled before benefits start.
Waiting periods for LTD benefits typically range from 30 days to 180 days. The waiting period is the time you must be disabled before you start receiving benefits.
Benefit Calculation and Payment
LTD benefits are typically calculated as a percentage of your pre-disability income. The percentage varies depending on the policy, but it is often around 60% to 80%. The maximum benefit amount is usually capped at a certain level, such as $10,000 per month.
LTD benefits are typically paid out monthly. The payments can be made directly to you or to your creditors, depending on the terms of your policy.
The Importance of Long-Term Disability Insurance

The financial security you’ve worked hard to build can be jeopardized by an unexpected disability. Long-term disability insurance acts as a safety net, providing financial support during a time when you’re unable to work due to a serious health condition. This insurance can help you maintain your lifestyle, pay your bills, and avoid financial strain.
The Financial Implications of a Long-Term Disability
A long-term disability can significantly impact your finances. Without a reliable income source, you may struggle to meet your basic needs. This can lead to:
- Loss of income: Your primary income source is disrupted, potentially causing a substantial reduction in your monthly earnings.
- Accumulation of debt: You may find yourself unable to make mortgage payments, car payments, or credit card bills, leading to a buildup of debt.
- Depletion of savings: You may be forced to dip into your savings to cover essential expenses, potentially eroding your financial security for the future.
- Financial strain: The lack of income can lead to financial stress and anxiety, impacting your overall well-being.
Common Disabilities that Could Necessitate Long-Term Coverage
Numerous health conditions can lead to a long-term disability. Some common examples include:
- Back injuries: Back pain and injuries can significantly limit your ability to perform daily tasks and work, potentially requiring extended periods of recovery.
- Cancer: Depending on the type and stage of cancer, treatment can involve surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation, leading to prolonged periods of recovery and potential limitations.
- Heart disease: Heart attacks, strokes, and other heart conditions can result in significant physical limitations, requiring extensive rehabilitation and potentially impacting your ability to work.
- Mental health conditions: Conditions like depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder can affect your ability to focus, concentrate, and perform work-related tasks, potentially leading to a long-term disability.
The Emotional and Psychological Impact of a Disability
A disability can have a profound emotional and psychological impact. It can lead to:
- Loss of identity: Your work often plays a significant role in your identity and sense of purpose. Losing your ability to work can lead to feelings of isolation and loss of self-worth.
- Depression and anxiety: The stress of dealing with a disability, financial strain, and potential changes in lifestyle can contribute to depression and anxiety.
- Social isolation: You may experience social isolation due to limitations in your ability to participate in activities or interact with friends and family.
- Anger and resentment: You may feel anger and resentment towards your situation, leading to emotional distress and difficulty coping with the changes.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Long-Term Disability Insurance
Choosing the right long-term disability insurance policy is crucial for protecting your income in case of a disabling illness or injury. It is essential to consider various factors that influence the coverage and benefits offered by different insurers.
Policy Features and Benefits
Insurers offer a range of policy features and benefits, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences is vital for making an informed decision.
- Definition of Disability: This refers to the criteria insurers use to determine whether a condition qualifies as a disability. Some policies may use a strict definition, requiring complete inability to work, while others may consider partial disability or limitations in specific job functions.
- Elimination Period: This is the waiting period before benefits start. A longer elimination period generally leads to lower premiums but means you’ll have to wait longer to receive benefits. It’s important to choose an elimination period that aligns with your financial situation and risk tolerance.
- Benefit Period: This refers to the duration for which benefits are paid. Policies may offer coverage for a specific period, such as five years, or for life. Choosing a benefit period that meets your long-term needs is essential.
- Benefit Amount: This is the amount of monthly benefit you receive. It’s generally a percentage of your gross income, with a maximum limit. A higher benefit amount provides greater financial security but may also result in higher premiums.
- Inflation Protection: This feature increases your benefit payments over time to account for inflation, ensuring your benefits keep pace with rising living costs. It is a valuable consideration for long-term disability insurance.
- Cost of Living Adjustment (COLA): This feature increases your benefit payments based on a specific index, such as the Consumer Price Index (CPI). COLA helps protect your purchasing power over time.
- Partial Disability Coverage: Some policies offer benefits for partial disability, meaning you can receive benefits if you are unable to perform some of your job duties. This can be helpful for individuals whose work involves specific tasks or skills.
- Residual Disability Coverage: This coverage provides benefits if you are unable to work at your usual occupation but can still perform some type of work. It can be helpful for individuals who can transition to a different job or work part-time.
- Waiver of Premium: This feature waives your premium payments if you become disabled, preventing the policy from lapsing. It can be a valuable protection, especially for individuals with a high risk of disability.
- Return to Work Benefits: Some policies offer benefits to help you return to work after a disability. This may include vocational rehabilitation services, job training, or financial incentives for finding a new job.
Key Considerations for Choosing a Policy
When choosing a long-term disability insurance policy, several key considerations can help you make an informed decision. These include:
| Factor | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Your Occupation | The nature of your work and the risk of disability associated with it. | Policies may have different coverage limits and premiums based on occupation. |
| Your Income | Your current income level and your projected future earnings. | The benefit amount should be sufficient to cover your living expenses and debts. |
| Your Age and Health | Your age and health status can affect both your eligibility and premium costs. | Younger and healthier individuals generally have lower premiums. |
| Your Financial Situation | Your current savings, investments, and debt levels. | Your financial resources can influence your need for disability insurance and the level of coverage you require. |
| Your Family Situation | Your dependents and their financial needs. | Consider the impact of a disability on your family’s financial security. |
| Your Risk Tolerance | Your willingness to accept risk and the level of financial protection you desire. | Higher risk tolerance may lead to choosing a policy with lower premiums but less comprehensive coverage. |
Determining the Appropriate Coverage Amount
The appropriate coverage amount for long-term disability insurance should be sufficient to replace your lost income and cover your living expenses. This typically involves calculating your gross income, including salary, bonuses, and other benefits. It is recommended to aim for a coverage amount that replaces at least 60% to 70% of your gross income.
A general rule of thumb is to aim for a coverage amount that replaces 60% to 70% of your gross income.
For example, if your gross income is $100,000 per year, a coverage amount of $60,000 to $70,000 per year would be appropriate. This will help ensure you have sufficient financial protection to cover your living expenses, including mortgage payments, utilities, food, transportation, and other essential costs.
Navigating the Application Process
Applying for long-term disability insurance can seem daunting, but understanding the process and gathering the necessary information can streamline the application and increase your chances of approval.
Application Requirements and Documentation
Before applying, gather the required documentation to ensure a smooth process. These documents typically include:
- Personal Information: This includes your name, address, date of birth, Social Security number, and contact information.
- Employment Information: Provide details about your employer, job title, salary, and start date. Include any relevant information about your job duties and responsibilities.
- Medical Records: This is crucial for supporting your claim. Obtain medical records from your doctor(s) detailing your condition, diagnosis, treatment history, and any limitations you experience.
- Financial Information: You may be asked to provide details about your income and expenses, particularly if you are seeking benefits for a specific period.
Tips for Maximizing Approval Chances
- Complete the Application Thoroughly and Accurately: Carefully read all instructions and provide detailed and accurate information. Any discrepancies or omissions can delay the process and potentially affect your claim.
- Seek Medical Documentation: Thorough medical documentation is essential. Ensure your medical records are complete, including diagnoses, treatment plans, and limitations.
- Consult with a Disability Insurance Specialist: A specialist can help you understand the application process, gather necessary documents, and navigate any potential challenges.
- Follow Up Regularly: Stay in contact with the insurance company to track the progress of your application and address any questions or concerns promptly.
Claiming Benefits

Navigating the process of claiming long-term disability benefits can feel overwhelming, but understanding the steps involved can help ease the process. It’s crucial to act promptly and follow the procedures Artikeld by your insurer to maximize your chances of a successful claim.
Filing a Disability Claim
When you become disabled and unable to work, you need to file a claim with your insurance company. This involves notifying them of your disability and providing the necessary documentation. The following steps Artikel the typical process:
- Contact your insurance company: Immediately notify your insurer about your disability, following their specific procedures.
- Complete claim forms: Your insurer will provide you with claim forms to complete, detailing your medical condition, disability, and employment information.
- Gather supporting documentation: This includes medical records, doctor’s notes, and any other relevant documents that support your claim.
- Submit your claim: Once you’ve completed the forms and gathered all the necessary documentation, submit your claim to your insurer.
Documentation and Evidence
To support your claim, you need to provide comprehensive and convincing documentation. This evidence will help the insurer assess your disability and determine your eligibility for benefits.
- Medical records: These are essential for establishing the nature and severity of your disability. They should include diagnosis, treatment history, and any limitations imposed by your condition.
- Doctor’s notes: These should provide detailed information about your disability, including your functional limitations, restrictions, and prognosis.
- Employment records: This includes your work history, job description, and any documentation of your earnings.
- Other relevant documentation: Depending on your situation, you might need to provide additional documentation such as:
- Disability evaluation reports: These reports, conducted by independent physicians, provide an objective assessment of your disability.
- Work capacity evaluations: These evaluations assess your ability to perform specific tasks and activities related to your job.
- Vocational rehabilitation reports: These reports evaluate your skills and training to determine your potential for retraining or alternative employment.
Appealing Denied Claims
If your claim is denied, you have the right to appeal the decision. This involves challenging the insurer’s decision and presenting additional evidence to support your claim.
- Review the denial letter: Carefully review the denial letter to understand the reasons for the denial.
- Gather additional evidence: This might include updated medical records, new evaluations, or any other documentation that strengthens your claim.
- File an appeal: Follow the insurer’s specific procedures for filing an appeal. This usually involves submitting a written appeal within a designated timeframe.
- Consider legal representation: In complex cases, consulting with a disability lawyer can be beneficial. They can help you navigate the appeals process and ensure your rights are protected.
Understanding Exclusions and Limitations
While disability insurance offers crucial financial protection during periods of disability, it’s essential to understand that policies often contain exclusions and limitations. These provisions specify situations where coverage may not apply, and it’s crucial to review them carefully before purchasing a policy.
Common Exclusions and Limitations
Exclusions and limitations in disability insurance policies are designed to prevent abuse and ensure the sustainability of the program. They typically cover situations that are not considered true disabilities, such as:
- Pre-existing conditions: Policies often exclude coverage for conditions that existed before the policy’s effective date. This means if you had a health issue prior to purchasing the policy, you might not be covered for related disabilities.
- Self-inflicted injuries: Disability insurance policies typically do not cover disabilities resulting from self-harm or intentional acts. This includes injuries caused by substance abuse or suicide attempts.
- War or acts of terrorism: Disabilities arising from war, acts of terrorism, or military service are usually excluded from coverage.
- Certain occupations: Some policies may exclude coverage for specific high-risk occupations, such as those involving hazardous materials or extreme physical exertion. This is due to the increased likelihood of disability in such professions.
- Cosmetic surgery: Policies generally do not cover disabilities resulting from elective cosmetic surgery. This is because such procedures are not considered medically necessary.
Activities or Conditions Not Covered
Disability insurance policies may also specify activities or conditions that are not covered. This can include:
- Recreational activities: While most policies cover disabilities resulting from accidents, they may exclude coverage for injuries sustained during risky recreational activities such as skydiving, rock climbing, or extreme sports.
- Mental health conditions: Some policies may have limitations on coverage for mental health conditions, especially if they are pre-existing or if treatment is not deemed medically necessary.
- Pregnancy and childbirth: Disability insurance policies typically do not cover disabilities related to pregnancy and childbirth, as these are considered normal biological processes.
Mitigating Risks and Ensuring Comprehensive Coverage
To mitigate potential risks and ensure comprehensive coverage, consider the following:
- Read the policy carefully: Thoroughly review the policy document, including all exclusions and limitations, before purchasing. Pay attention to specific conditions, activities, and occupations that may be excluded.
- Consider a rider: Some policies offer riders that can extend coverage for specific conditions or activities. These riders can provide additional protection for pre-existing conditions, mental health issues, or recreational activities.
- Seek professional advice: Consult with an insurance broker or financial advisor who specializes in disability insurance. They can help you understand the policy’s provisions, identify potential risks, and select the most appropriate coverage for your needs.
The Role of Employers and Group Plans
Many employers offer long-term disability insurance as part of their benefits package. These plans are often a valuable resource for employees, providing financial security in the event of a long-term disability.
Group plans offer several advantages, including:
Employer Contributions
Employer-sponsored plans often involve employer contributions, reducing the cost of coverage for employees. This can be a significant financial benefit, making it more affordable to secure adequate coverage. For example, an employer might contribute 50% of the premium for a group long-term disability plan, reducing the employee’s out-of-pocket expenses.
Group Rates
Group plans typically offer lower premiums than individual policies. This is because insurance companies can spread the risk across a larger pool of insured individuals, leading to lower costs for each participant.
Simplified Application Process
Applying for group coverage is often simpler than applying for individual policies. Employers handle the administrative aspects of the application process, making it more convenient for employees.
Potential Tax Advantages
In some cases, employer contributions to group disability insurance plans may be tax-deductible for the employer, while employee premiums may be tax-deductible for the employee. This can further reduce the overall cost of coverage.
Group Plans vs. Individual Policies
While group plans offer numerous advantages, it’s essential to consider the potential drawbacks:
Limited Coverage Options
Group plans may have limited coverage options compared to individual policies. For example, they might offer a lower benefit amount or have stricter eligibility requirements.
Potential for Coverage Gaps
Group coverage ends when an employee leaves their job. This can create a coverage gap if the individual doesn’t have an alternative disability insurance policy in place.
Employer Influence
Employers may have some control over the terms of the group plan, including the coverage level and benefits. This could limit an employee’s ability to tailor coverage to their specific needs.
Understanding Employer Contributions and Benefits
It’s crucial for employees to understand the details of their employer-sponsored disability insurance plan. This includes:
Benefit Amount
The amount of the monthly benefit payable in the event of a disability.
Waiting Period
The period of time an employee must be disabled before benefits begin.
Elimination Period
The period of time an employee must be disabled before benefits begin.
Maximum Benefit Period
The length of time benefits are payable.
Exclusions and Limitations
Specific conditions or situations that are not covered by the policy.
Claim Process
The procedures for filing a claim and receiving benefits.
By understanding these details, employees can ensure that their employer-sponsored disability insurance plan meets their needs and provides adequate financial protection in the event of a long-term disability.
Financial Planning and Long-Term Disability
Disability insurance is a crucial component of a comprehensive financial plan, providing a safety net in case of unforeseen circumstances that prevent you from working. Integrating disability insurance into your financial strategy can help mitigate potential financial hardship and protect your future.
Incorporating Disability Insurance into Financial Planning
It is essential to consider disability insurance as part of your overall financial planning. Disability insurance can help you maintain your standard of living and cover essential expenses, such as mortgage payments, utilities, and healthcare costs, if you become disabled and unable to work.
- Determine your coverage needs. Consider your income, expenses, and dependents when calculating the amount of disability insurance you need. A general rule of thumb is to aim for coverage that replaces 60-80% of your gross income.
- Choose the right type of coverage. There are various types of disability insurance available, including individual and group policies. Consider your specific needs and budget when selecting the most suitable coverage.
- Review and update your coverage periodically. As your income, expenses, and family situation change, it’s important to review and update your disability insurance coverage to ensure it continues to meet your needs.
Reviewing and Updating Coverage Needs
Periodically reviewing your disability insurance coverage is crucial to ensure it remains adequate. Factors that may necessitate a review include:
- Changes in income: Promotions, salary increases, or career changes can affect your coverage needs. It is advisable to adjust your coverage to reflect your current income level.
- Changes in expenses: As your family grows or your expenses increase, you may need to adjust your coverage to ensure it adequately protects your financial stability.
- Changes in health status: If you develop a pre-existing condition, it is important to review your coverage to ensure it includes appropriate benefits.
Managing Finances During a Disability
Managing finances during a disability can be challenging. Here are some tips to help you navigate this period:
- Create a budget: Develop a detailed budget that accounts for all your essential expenses, such as housing, utilities, groceries, and healthcare costs.
- Reduce unnecessary expenses: Identify areas where you can cut back on spending, such as dining out, entertainment, and non-essential subscriptions.
- Explore alternative income sources: Consider part-time work or other income-generating activities that you can perform despite your disability.
- Seek financial counseling: If you are struggling to manage your finances, consult with a financial advisor or credit counselor for personalized guidance.
Resources and Support for Disability Insurance
Navigating the complexities of disability insurance can be daunting, but there are numerous resources available to provide guidance and support. From reputable organizations to qualified professionals, these resources can empower you to make informed decisions and navigate the process with confidence.
Reputable Organizations and Resources
Reputable organizations and resources can provide valuable insights into disability insurance, helping you understand your options and make informed decisions.
- The National Disability Institute (NDI): NDI is a non-profit organization dedicated to improving the lives of people with disabilities. They offer a wealth of information on disability insurance, including resources for individuals, employers, and policymakers.
- The Council for Disability Awareness (CDA): CDA is a non-profit organization that provides education and advocacy on disability insurance. They offer a range of resources, including articles, webinars, and a disability insurance glossary.
- The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC): NAIC is a non-profit organization that regulates the insurance industry in the United States. Their website offers information on state insurance laws and regulations, including those related to disability insurance.
- The Social Security Administration (SSA): SSA administers Social Security benefits, including disability benefits. Their website provides information on eligibility requirements, application procedures, and benefit amounts.
- The U.S. Department of Labor: The Department of Labor offers resources on disability insurance, including information on employer-sponsored plans and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA).
Finding Qualified Financial Advisors and Insurance Brokers
Finding qualified financial advisors and insurance brokers is crucial to ensure you receive appropriate advice and guidance on disability insurance.
- Seek Recommendations: Ask friends, family, and colleagues for recommendations of trusted financial advisors and insurance brokers.
- Check Credentials: Verify the credentials and licenses of potential advisors and brokers. Look for designations such as Certified Financial Planner (CFP), Chartered Financial Consultant (ChFC), or Registered Financial Consultant (RFC).
- Consider Experience: Seek advisors and brokers with experience in disability insurance.
- Request References: Ask for references from previous clients to gain insights into their experience with the advisor or broker.
- Meet with Multiple Professionals: Meet with several advisors and brokers to compare their approaches, expertise, and fees.
Navigating the Complexities of Disability Insurance
Navigating the complexities of disability insurance can be challenging, but there are strategies to simplify the process.
- Start Early: Begin researching and planning for disability insurance early in your career.
- Understand Your Needs: Determine your specific needs and financial goals to identify the appropriate coverage.
- Compare Policies: Obtain quotes from multiple insurance companies and compare policy features, coverage, and premiums.
- Ask Questions: Don’t hesitate to ask questions about policy terms, exclusions, and limitations.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult with a qualified financial advisor or insurance broker to receive personalized guidance.
Closing Notes
Navigating the complexities of long-term disability insurance can feel daunting, but with a clear understanding of the key factors, the process becomes more manageable. From understanding the types of coverage available to navigating the application and claims process, this guide provides a roadmap for securing the financial protection you need. Remember, taking proactive steps to secure your future can provide peace of mind and a sense of security in the face of life’s unexpected turns.